Stroke is a neurological disorder characterized by blockage of blood vessels. Clots form in the brain and interrupt blood flow, clogging arteries and causing blood vessels to break, leading to bleeding. Rupture of the arteries leading to the brain during stroke results in the sudden death of brain cells owing to a lack of oxygen. Stroke can also lead to depression and dementia.
What Are The Different Types Of Stroke?
Strokes can be classified into 2 main categories:
- Ischemic strokes. These are strokes caused by blockage of an artery (or, in rare instances, a vein). About 87% of all strokes are ischemic.
- Hemorrhagic These are strokes caused by bleeding. About 13% of all strokes are hemorrhagic.
What Are The Symptoms Of An Ischemic Stroke?
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of your face and body
- Aphasia (trouble speaking or a complete loss of speech)
- Slurred or garbled speaking (dysarthria)
- Loss of muscle control on one side of your face
- Sudden worsening or loss of your senses (including vision, hearing, smell, taste and touch)
- Blurry vision or double vision (diplopia)
- Loss of coordination or clumsiness (ataxia)
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Nausea and vomiting
- Neck stiffness
- Mood swings or sudden personality changes
- Confusion or agitation
- Seizures
- Memory loss (amnesia)
- Headaches (usually sudden and severe)
- Passing out or fainting
- Coma
Symptoms Of Hemorrhagic Stroke
- severe headache
- paralysis on one side
- facial numbness or loss of movement on one side
- trouble speaking
- problems with coordination
- muscle weakness or paralysis
- vomiting
- neck stiffness
- increased blood pressure
- seizure
- partial blindness
- visual changes
- drooping eyelids
Recognizing Stroke: The BE FAST Method

When it comes to identifying a stroke, acting quickly can make all the difference. Use the acronym BE FAST to remember the key warning signs:
B – Balance
Be alert for a sudden loss of balance or
E – Eyes
Sudden changes in vision, including partial or complete loss in one or both eyes, could be a red
F – Face
Smile and check for One side of the face may appear uneven or drooped.
A – Arms
Lift both If one arm sags or drops involuntarily, it could indicate muscle weakness due to a stroke.
S – Speech
Slurred speech, difficulty speaking, or trouble finding the right words are common
T – Time
Time is critical! Call for emergency medical help immediately. Note the exact time symptoms started, as this information can guide healthcare providers in selecting the most effective treatment options.
For Stroke Dr. Sri Ranjani Bhat can guide you through the most suitable therapies and medications for your specific needs.
Also, Read – Ayurvedic Treatment for Diabetes | Ayurveda for Diabetes
AYURVEDA PERSPECTIVE ON STROKE
With the review of Ayurvedic literature, it is evident that no specific etiological factor described separately for Pakshaghata(stroke). So all factors vitiating Vata Dosha in body are root cause of Pakshaghata.
- Aharajanya Factors – related to food
- Viharajanya Factors – behavioural factors
- Manasa Factors – emotional factors
- Abhighataj Factors – traumatic factors
- Anya Factors- other factors like seasonal variation
AYURVEDIC TREATMENT FOR BRAIN STROKE
1) Snehana(Oleation Therapy)
Snehana can be achieved by two ways: internal oleation and external oleation.
Internal Oleation (Snehana)
Snehana, or internal oleation, is the first and foremost line of treatment in the management of Pakshaghata (hemiplegia), as described in Ayurvedic texts. This process involves the administration of lipids such as Ghrita (ghee), Taila (oil), Vasa (muscle fat), or Majja (bone marrow), which are selected based on the patient’s dosha imbalance and digestive capacity.
Role of Internal Oleation in Pakshaghata
In Pakshaghata, the vitiation of Vata Dosha plays a central role. Snehana helps pacify this aggravated Vata with its inherent Snigdha (unctuous), Picchila (sticky), and Guru (heavy) qualities. These lipids are hydrophilic in nature and work at the cellular level, saturating body cells with fats. Through the process of osmosis, the fats are transported to extracellular fluids, increasing plasma volume. To restore equilibrium, the excess fluid moves to the gastrointestinal tract, preparing the body for the elimination of toxins (Doshas) through therapeutic purgation or emesis.
Selection of Sneha Based on Dosha Imbalance
1. Vata-Pitta Imbalance:
Ghrita is the preferred lipid for internal oleation in patients where Vata is associated with Pitta
Dosha. Specific formulations like Sarvaamyaantak Ghrita, Nakuladi Ghrita, Brahitchagaladi Ghrita, and Hansadi Ghrita are highly recommended for their cooling and soothing properties.
2. Vata-Kapha Imbalance
In cases where Vata is accompanied by Kapha Dosha, Taila (oil) is the ideal choice for oleation. Some effective oils include:
- Balaashwagandhaadi Taila
- Karpasasthyadi Taila
- Narayan Taila
- Nakul Taila
- Masha Taila
3. Use of Vasa and Majja
When the patient’s Agni (digestive fire) is robust, Vasa and Majja can also be used for internal oleation, offering profound nourishment and support for Vata pacification.
External Oleation: A Supportive Therapy for Pakshaghata
In Ayurvedic management, external oleation is a complementary treatment modality for Pakshaghata (hemiplegia). This therapy involves the application of medicated oils externally to nourish the body, strengthen muscles, and restore balance in the nervous system. Two primary methods of external oleation are Abhyanga (therapeutic massage) and Moordhini Taila (head oil therapies).
Abhyanga: Oil massage
Abhyanga involves massaging the body with specific medicated oils tailored to the patient’s condition. Oils such as:
- Masha Taila
- Mahamasha Taila
- Nakul Taila
- Narayana Taila
- Shatavari Taila
- Vishgarbha Taila (used strictly for external application as it contains toxic substances like Dhatura and Vatsnabha)
These oils are carefully chosen for their ability to alleviate Dhatukshaya (tissue depletion), which is commonly observed in Pakshaghata. Regular Abhyanga enhances blood circulation, delivering fresh oxygenated blood to the muscles, which aids in their nourishment and strengthening.
Moordhini Taila: Rejuvenation for the Nervous System

Moordhini Taila refers to the application of oil to the head and is particularly effective in addressing neurological symptoms of Pakshaghata, such as speech impairments. This therapy is classified into four types:
- Shirobasti: Retention of oil on the head using a specialized
- Shiropichu: Keeping a soaked cotton pad on the crown of the
- Shiroseka: Continuous pouring of warm medicated oil over the
- Shiro Abhyanga: Gentle head massage with medicated
The unique properties of Moordhini Taila not only combat Swarbalam (speech disturbances) but also help maintain equilibrium in the nervous system.
2. Swedana Therapy (Fomentation Therapy)
Swedana, or fomentation therapy, is a vital component of Ayurvedic treatments, known for its ability to alleviate Vata Dosha, reduce stiffness, and strengthen muscles. This therapeutic application of heat plays a significant role in conditions such as Pakshaghata (hemiplegia) and other neurological disorders, providing both relief and rejuvenation.
Types of Swedana Therapy
Several methods of Swedana therapy can be employed based on the patient’s condition:
- Nadi Sweda: Steam is applied to specific areas using a tube or
- Pinda Sweda: A unique therapy that involves applying heated Subtypes include:
- Patrapinda Sweda: Using boluses prepared with medicinal
- Shashtikashali Pinda Sweda: Utilizing boluses made of medicinal rice cooked in milk and herbal decoctions.
- Parisheka Sweda: Pouring warm medicated liquids over the body in a continuous
- Awagaha Sweda: Immersing the body or affected parts in medicated decoctions or
- Upanaha Sweda: Applying medicated poultices over the affected Subtypes include:
- Shalvana Upanaha Sweda: Using herbal ingredients for
- Mahashalvana Upanaha Sweda: A more potent formulation for deeper
3. Vamana(Emesis)
Mild Vamana is indicated in the treatment of Pakshaghata.
4. Virechana(Purgation Therapy)
Virechana, or purgation therapy, is one of the most effective treatments in Ayurveda for detoxification and balancing the body’s energies. Ayurvedic classics recommend Mridu Virechana (mild purgation) for individuals suffering from Pakshaghata. The use of Gandharvahasta Taila, a medicated oil known for its gentle purgative properties, is advocated for this purpose.
Benefits of Virechana Karma
- Detoxification: Removes toxins (Ama) from the gastrointestinal tract, promoting overall
- Balance of Doshas: Specifically pacifies Pitta Dosha, which is often aggravated in
- Neuro-Enhancement: Improves the action of neuropeptides, enhancing brain and nervous system functions.
- Tissue Rejuvenation: Strengthens Rakta Dhatu and its associated sub-tissues (Sira and Snayu), aiding in recovery from paralysis and other neurological conditions.
- Basti(Medicated Enema)
In Ayurveda, Basti Chikitsa is revered as the most effective treatment modality for managing Vata Dosha, which governs movement and communication in the body. This therapy involves the administration of medicated enemas. The vitiation of Vata Dosha is considered a root cause of numerous diseases. Basti, by virtue of its direct action on the gastrointestinal tract and deeper tissues, effectively balances and pacifies Vata Dosha.
Classical Ayurvedic texts mention a variety of Basti formulations designed to treat Vata-related disorders. Some of the commonly recommended preparations include:
- Rasnadi Asthapana Basti
- Guduchi Triphaladi Asthapana Basti
- Anuvasana Basti with medicated oils like:
- Masha Taila
- Mahamasha Taila
- Nakul Taila
- Prabhanjan Vimardan Taila
- Sarvaamyaantak Taila
Each of these formulations is tailored to address specific manifestations of Vata imbalance, such as pain, stiffness, or neurological deficits.
Suggested – Virechana Treatment: Procedure, Types, Benefits, and Precautions
The Gut-Brain Connection in Basti Therapy
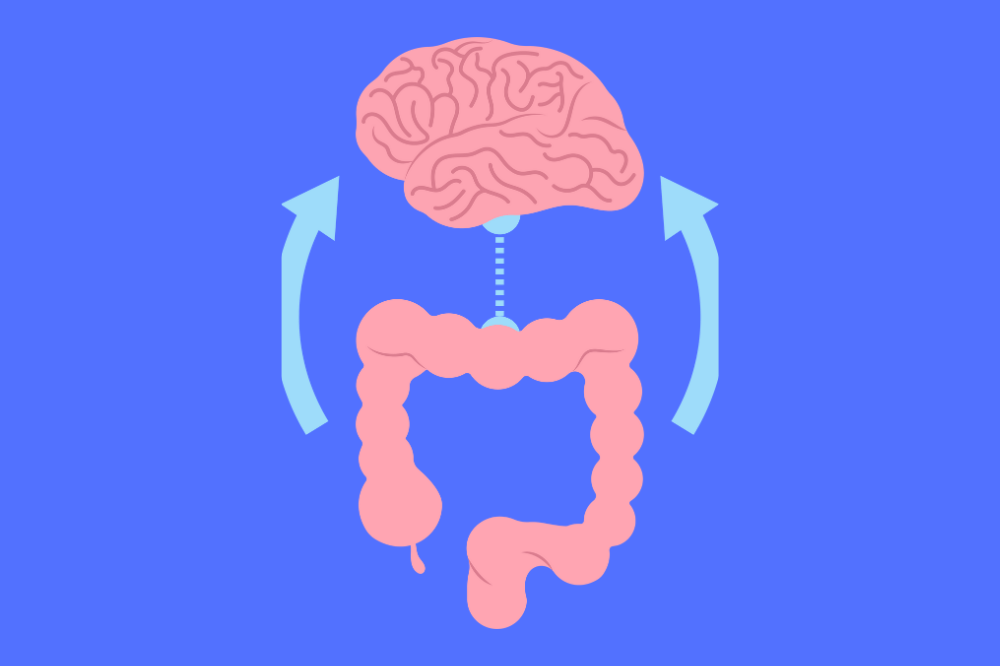
Modern research has revealed the intricate relationship between the Enteric Nervous System (ENS) and the Central Nervous System (CNS). Often referred to as the “gut-brain axis”, this network highlights how closely the gastrointestinal system is linked to overall brain function.
The ENS, located within the gastrointestinal tract, communicates with the CNS, working in perfect synergy to regulate bodily functions. By administering medicated enemas through Basti Karma, the ENS is stimulated, which in turn activates the CNS. This dynamic interaction enhances neurological function and fosters healing in conditions associated with Vata imbalances.
- Nasya Karma (Errhine Therapy) holds a special place among the Panchakarma treatments. This therapy involves administering medicated substances through the nostrils, making it a powerful and effective method for treating disorders of the head, neck, and central nervous system.
Why Nasya? The Nose as the Gateway
Ayurvedic texts emphasize that the nose is the gateway to Shira (head). This concept highlights the profound connection between the nasal passages and the central nervous system. When medicated substances are administered through the nostrils, they travel directly to the head, targeting the vitiated Doshas (imbalances) and eliminating toxins from the Shira region.
The drugs administered through the nostrils stimulate higher centers of the brain via the olfactory nerve pathway, which is intricately connected to the hypothalamus and limbic system.
- Olfactory Nerve Pathway: Acts as a direct channel to the brain, bypassing the blood-brain
- Hypothalamus Stimulation: Regulates vital functions such as hormone secretion, body temperature, and emotional responses.
- Limbic System Activation: Influences mood, memory, and behavior, promoting mental clarity and emotional stability.
By utilizing this pathway, Nasya therapy delivers targeted and rapid effects, making it a unique treatment modality for conditions involving the central nervous system (CNS).
8) Raktamokshana(Blood Letting) can be done when numbness is present.
INTERNAL MEDICINES
1. Kwatha Kalpana (Decoctions)
Decoctions are prepared with herbal combinations to balance Vata Dosha and support recovery:
- Balaadi Kwatha
- Gokshuradi Kwatha
- Mashabalaadi Kwatha
- Rasnadashmooladi Kwatha
- Maharasnadi Kwatha
- Sahacharadi Kwatha
- Mashaatmaguptadi Kwatha
2. Ghrita Kalpana (Medicated Ghee)
Medicated ghees are used to nourish the brain and improve neurological functions:
- Nakuladi Ghrita
- Brhitchagaladi Ghrita
- Hansadi Ghrita
- Brahmi Ghrita: Specifically beneficial for improving speech (Vaak Shuddhi) in patients with speech difficulty.
3. Taila Kalpana (Medicated Oils)
Oils are applied externally or used internally to manage Vata Dosha:
- Sidhartaka Taila
- Vishnu Taila
- Bala Taila
- Prasarini Taila
- Narayan Taila
- Laghuvishgarbha Taila
- Dhanwantra Taila
- Ksheerbala Taila
4. Choorna Kalpana (Powders)
Powders help balance Vata and alleviate symptoms:
- Rasnadi Choorna: Useful in all 80 Vataja Nanatamaja Vikaras (diseases caused by Vata).
5. Guggulu Preparations
Guggulu formulations strengthen joints and nerves:
- Dwatrinshak Guggulu
- Yograj Guggulu
- Tryodashanga Guggulu
6. Arishta Kalpana (Fermented Herbal Formulations)
Arishtas improve strength and promote recovery:
- Ashwagandhadi Arishta
- Bala Arishta
7. Leha Kalpana (Herbal Jams)
Leha formulations provide nourishment and enhance speech functions:
- Kalyanaka Leha: Effective in managing speech
8. Ras Aushadhi (Herbo-Mineral Preparations)
These formulations are potent for managing Vata disorders:
- Swachand Bhairav Rasa
- Vatavidhvansa Rasa
- Vatarakshasa Rasa
- Pratapagnikumar Rasa
- Lakshminarayan Rasa
- Vatari Rasa
- Vatagajankusha Rasa
- Mahavatagajankush Rasa
- Chintamani Rasa
- Brhitvatachintamani Rasa
- Lagvaananda Rasa
9. Single Herbs
Certain single drugs are highly effective in managing Pakshaghata:
- Ashwagandha: Strengthens nerves and
- Brahmi: Enhances cognitive
- Eranda: Pacifies Vata Dosha and reduces
- Rasona (Garlic): Improves circulation and reduces
- Rasna: Relieves pain and stiffness in joints and
Ayursh: Your Path to Comprehensive Ayurvedic Care
Ayursh Ayurveda stands at the forefront of Ayurvedic stroke care, seamlessly blending the time-tested principles of Ayurveda with modern medical advancements to provide a holistic path to recovery. With its patient- centered and integrative approach, Ayursh addresses the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of stroke rehabilitation, offering tailored solutions that promote overall healing and well-being.
Through therapies like Panchakarma, customized herbal remedies, and specialized rehabilitative techniques, Ayursh empowers patients to regain their vitality and quality of life. Our team of specialist doctors, with their deep expertise in Ayurveda and stroke care, will guide and assist you at every step of your recovery journey, ensuring personalized attention and effective treatment outcomes.
Remember, timely emergency medical attention is crucial in the event of a stroke, and Ayurveda offers a valuable complementary path to recovery and long-term wellness.
Download our app for ayurvedic treatment and therapies.
FAQs
1. What is a stroke?
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting the oxygen and nutrients it needs. This can lead to brain damage and loss of function.
2. What causes a stroke?
Common causes include:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Heart disease
3. What are the warning signs of a stroke?
Use the acronym FAST: F: Face drooping
A: Arm weakness S: Speech difficulty
T: Time to call emergency services
4. Are there any side effects of Ayurvedic treatments for Pakshaghata?
When administered by qualified Ayurvedic practitioners, treatments are safe and focus on restoring natural balance without significant side effects.
5. Can Ayurveda be combined with modern stroke treatments?
Absolutely. Ayurveda complements modern medical treatments by enhancing recovery, improving strength and mobility, and addressing long-term health maintenance. Emergency care should always be sought initially in a stroke event.
6. Do you have specialist doctors for stroke treatment?
Yes, at Ayursh, we have highly qualified specialist doctors who tailor treatment plans to individual needs, ensuring expert guidance and comprehensive care throughout the recovery process.
7. How long does it take to recover from Pakshaghata with Ayurveda?
Recovery depends on the severity of the condition, the patient’s age, and overall health. Ayurvedic treatments typically focus on gradual and sustained improvement in mobility, speech, and quality of life over weeks to months.
8. How does Ayurveda prevent future strokes?
Ayurveda emphasizes lifestyle changes, stress management, dietary modifications, and regular detoxification therapies like Panchakarma to maintain dosha balance and prevent recurrence.



